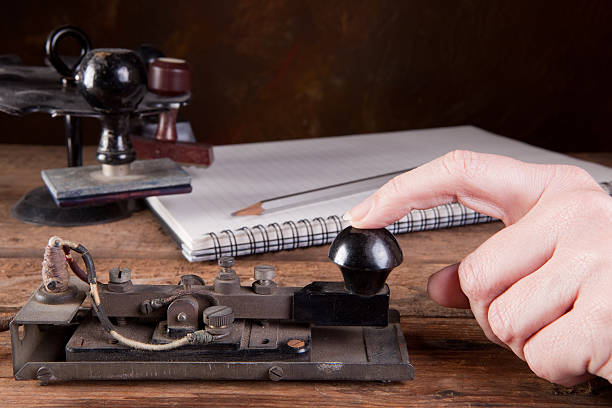
The telegraph was a wonderful invention that changed how people communicated over long distances. It all began in the early 19th century when Samuel Morse wanted to find a faster way to send messages.
He and his team developed a device called the telegraph, which used electrical signals to send coded messages through wires over great distances.
The key to the telegraph was Morse code, a special system of dots and dashes that represented letters and numbers. People learned how to tap out messages using this code, and telegraph operators could decode them on the other end.
The first successful telegraph line in the United States ran from Washington, D.C., to Baltimore, Maryland, and the very first message sent was “What hath God wrought?” It was a significant occasion that showed the world what technology could do.
Over time, telegraph lines spread across continents, connecting cities and countries. It became an essential tool for businesses, governments, and news organizations to quickly share information.
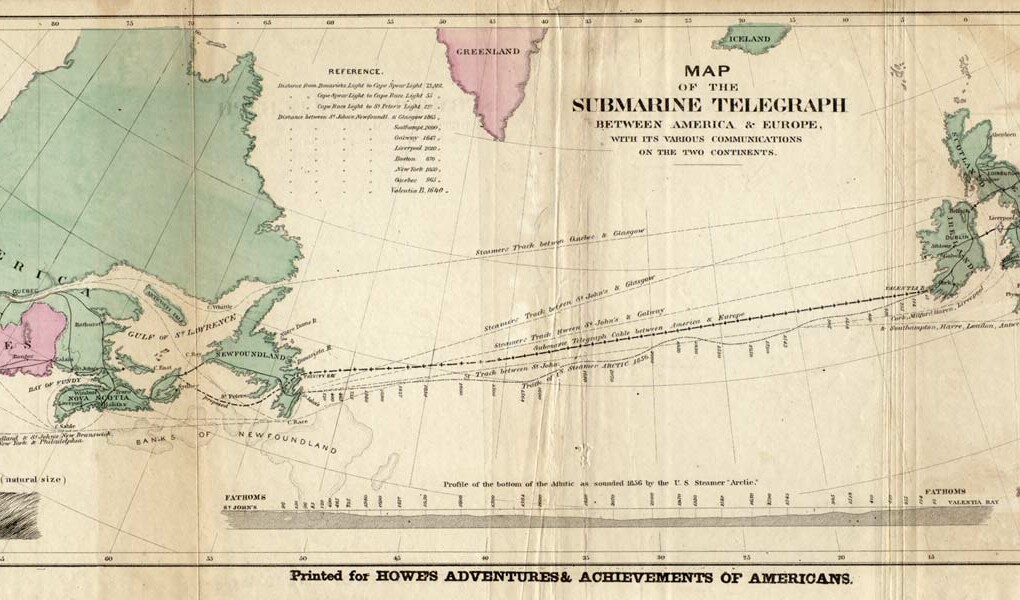
Later on, the telegraph paved the way for even more advanced forms of communication, like the telephone and eventually the internet. But it all started with Samuel Morse’s brilliant idea to harness electricity for sending messages quickly and efficiently.
The telegraph is a remarkable invention that brought people closer together across great distances and changed the world forever.